How to Extract Twitter Data Without Official API Access
How to Extract Twitter Data Without Official API Access
Extracting data from Twitter has become challenging due to expensive API pricing and strict limitations. Here's how you can gather Twitter data without relying on the official API:
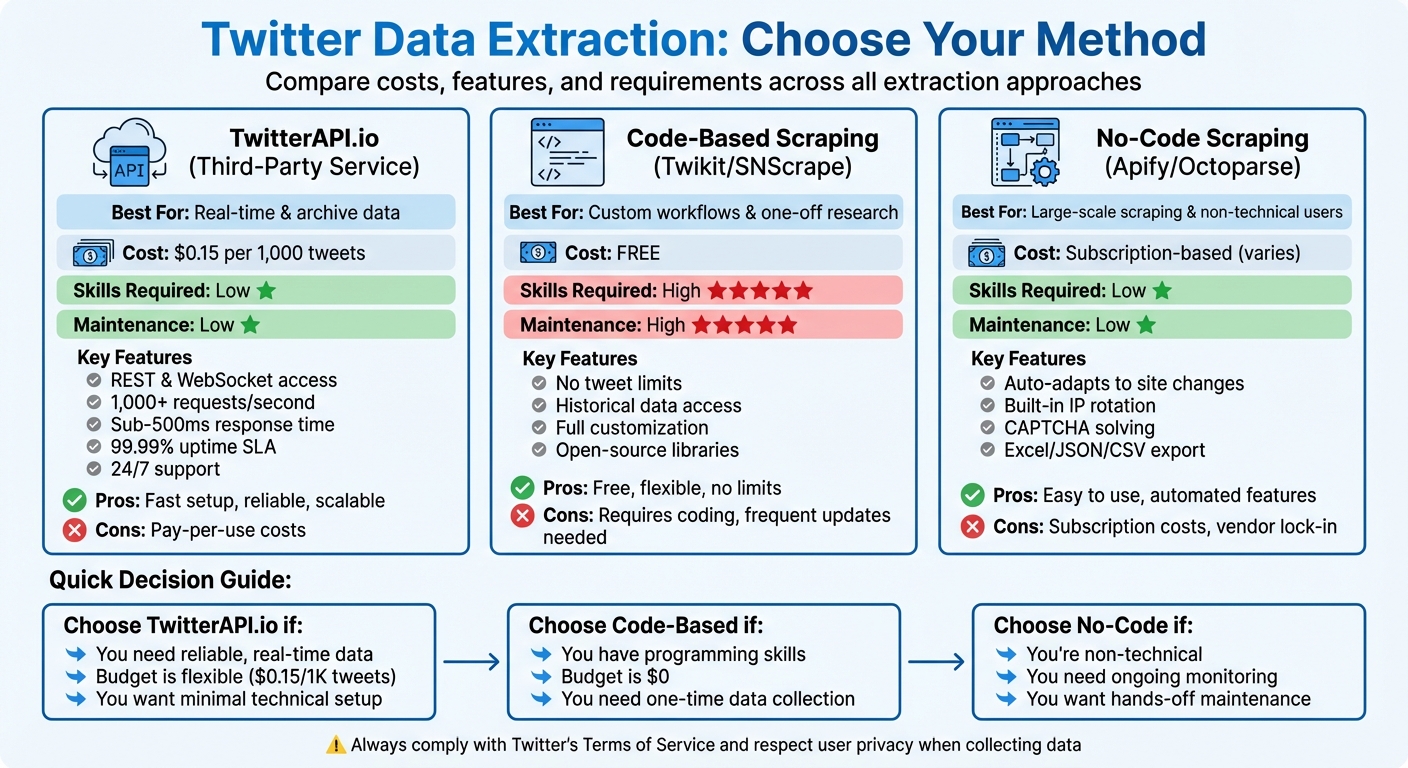
- Use Third-Party Services: Platforms like TwitterAPI.io offer affordable, pay-as-you-go options starting at $0.15 per 1,000 tweets. They provide REST and WebSocket access, support for real-time data, historical archives, and additional features like posting tweets or retrieving user profiles.
- Leverage Web Scraping: Tools like Twikit (Python library) or browser automation platforms such as Apify allow data extraction directly from Twitter's interface. These methods bypass API restrictions and are ideal for collecting large datasets.
- Code vs. No-Code Options: Developers can use open-source libraries like SNScrape or Twikit for custom workflows, while non-programmers can rely on no-code platforms like Apify for ease of use.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Always adhere to Twitter's Terms of Service, avoid scraping restricted sections, and prioritize user privacy by collecting only public data.
Quick Tip: If you're on a budget or need flexibility, third-party services like TwitterAPI.io are a practical solution. For one-off research, open-source tools might be sufficient, but they require technical skills.
Table Comparison:
| Method | Best For | Cost | Skills Required | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TwitterAPI.io | Real-time & archive | $0.15/1,000 tweets | Low | Low |
| Twikit (Code-Based) | Custom workflows | Free | High | High |
| Apify (No-Code) | Large-scale scraping | Subscription-based | Low | Low |
Each method has pros and cons, so choose based on your needs, technical expertise, and budget. Always stay compliant with legal guidelines to avoid potential issues.
Twitter Data Extraction Methods Comparison: Cost, Skills & Features
How To Scrape TWEETS WITHOUT Using Twitter API in Python.
How to Use TwitterAPI.io for Twitter Data Extraction

TwitterAPI.io offers a practical and budget-friendly alternative to Twitter's official API, cutting through the red tape and letting you access Twitter data in just five minutes. The platform operates on a straightforward pay-as-you-go model, charging only $0.15 for every 1,000 tweets - making it about 100 times more affordable than other options.
Getting Started with TwitterAPI.io
To get started, create a free account and instantly receive your API key. This grants you access to both REST and WebSocket endpoints. New users are even given $0.10 in credits to test the service - no credit card required. TwitterAPI.io simplifies integration by providing Swagger documentation, Postman collections, and pre-written code snippets.
"TwitterAPI.io saved us months of development time. The data quality and speed are unmatched." – Alex Chen, AI Researcher, Stanford
For those working on real-time applications, the platform offers WebSocket and webhook support, ensuring live data streams with sub-second latency. Additionally, TwitterAPI.io supports actions like posting tweets, liking, retweeting, and sending direct messages - features that can cost thousands of dollars per month through the official API. Academic users can email hello@twitterapi.io from their .edu address with a project description to unlock special rates tailored for research.
Once you're set up, you can dive into TwitterAPI.io's advanced features for efficient data extraction.
Main Features of TwitterAPI.io
TwitterAPI.io is designed to handle both live data streams and historical tweet archives, powered by a global infrastructure spanning over 12 regions. With the ability to process 1,000+ requests per second, sub-500 millisecond response times, and a 99.99% uptime SLA with automatic failover, the platform is built for high-demand scenarios. Users also benefit from around-the-clock live chat support.
With over 1,000,000 API calls successfully processed, the platform has demonstrated its reliability. Advanced search endpoints allow users to filter data by keywords, dates, and other specific metrics. The service also provides specialized access to data on Trends, Spaces, Communities, and List memberships. Keep in mind, there’s a minimum charge of $0.00015 per request, even if no data is returned.
Here’s a closer look at the pricing plans that make TwitterAPI.io suitable for a range of needs.
TwitterAPI.io Pricing Plans Breakdown
| Plan Type | Pricing Structure | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Pay-as-you-go | $0.15 per 1,000 tweets $0.18 per 1,000 user profiles $0.15 per 1,000 followers |
REST & WebSocket access, no monthly fees, 1,000+ requests/second, 24/7 support |
| Academic | Discounted rates (contact for quote) | Full archive access, research-friendly pricing, requires .edu email verification |
| Enterprise | Custom pricing | 99.99% uptime SLA, dedicated account manager, custom rate limits, priority support |
The pay-as-you-go model is particularly appealing for projects of any scale, as it eliminates the need for monthly fees and offers flexibility.
Web Scraping Methods for Twitter Data
If you’re looking for alternatives to TwitterAPI.io, web scraping can be a practical option for extracting Twitter data. This approach becomes especially useful when API access is limited or impractical. With over 500 million tweets posted daily on X.com, web scraping tools can tap into this vast pool of data - without the $100 monthly fee.
Using Twikit Library to Scrape Tweets
Twikit is an open-source Python library that connects directly to Twitter's internal API, bypassing the need for an official API key. To get started, install it using pip install twikit. After that, initialize the client with Client('en-US') and log in with your credentials. To avoid frequent reauthentication and minimize the risk of bans, save and reload your cookies.
Once authenticated, you can:
- Search for recent tweets with
await client.search_tweet('keyword', 'Latest') - Retrieve user profiles using
client.get_user_by_screen_name('username') - Monitor trending topics via
await client.get_trends('trending')
For storing the data, you can use the pandas library to convert the scraped tweets into DataFrames for analysis. Twikit is particularly effective for large-scale data collection, as it circumvents the restrictions of Twitter’s official API.
Browser Automation Tools for Non-Programmers
For those who don’t code, platforms like the Apify Store offer pre-configured scrapers. All you need to do is input a keyword or URL, and the tool will deliver results in formats like Excel, JSON, or CSV. These tools handle proxy rotation, CAPTCHA solving, and anti-bot measures automatically.
Another option is Browserless, which provides a "/scrape" REST API and "BrowserQL" for simplified data extraction without needing to write Puppeteer scripts. To avoid detection, stealth browsers like Kameleo can rotate dynamic fingerprints and simulate real user behavior. Kameleo’s plans range from Free (60 requests per minute) to Enterprise (1,200 requests per minute), with some customers managing up to 1.2 million browser instances daily.
"Instead of a traditional Twitter scraper API, you run a real browser, load a Twitter profile, and extract data from the rendered DOM." – Alejandro Loyola, Technical Support, Browserless
To keep your scraping efforts under the radar, introduce a 2-second delay between requests and use rotating residential proxies. For consistent data collection, schedule runs using cron jobs or no-code tool schedulers. Additionally, storing post IDs and timestamps can help deduplicate data, saving both time and resources.
The following section will compare these methods to help you decide which approach suits your needs best.
Code-Based vs. No-Code Scraping: Comparison
Code-based tools like Twikit or Snscrape offer maximum control and flexibility, making them ideal for custom workflows. However, they require a significant time investment to maintain, as Twitter’s layout changes frequently. These tools are free and can access historical data, making them perfect for smaller projects or one-off research.
On the other hand, no-code platforms like Apify or Octoparse are designed for ease of use. They automatically adapt to site changes and include features like IP rotation, which you’d otherwise need to implement manually. These platforms are better suited for large-scale data collection or ongoing monitoring, especially if you don’t have a developer to maintain scripts.
| Method | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code-Based (Twikit/Snscrape) | Custom/One-off research | Free, no tweet limits, historical data | Requires coding skills, high maintenance |
| No-Code (Apify/Octoparse) | Scaling/Non-technical users | Low maintenance, built-in anti-bot features | Subscription costs, vendor lock-in |
| DIY Headless (using Selenium) | Complex browser interactions | Full control over UI actions | High proxy costs, fragile to site updates |
"For one-off research, open-source is a great option. For ongoing Twitter data scraping, paid web scraping tools can reduce breakage and hidden costs." – Cem Dilmegani, Principal Analyst, AIMultiple
If you need precise custom logic and want to avoid per-request fees, go for code-based tools. But if you’re scaling operations or don’t want the hassle of script maintenance, managed no-code solutions are the way to go.
sbb-itb-9cf686c
Legal and Ethical Guidelines for Twitter Data Extraction
When it comes to extracting data from Twitter, understanding the legal and ethical boundaries is just as important as knowing the technical methods. Before diving into data collection, take time to review the rules and regulations. For instance, Twitter's Terms of Service explicitly prohibit scraping their platform without prior consent. Ignoring these terms could result in consequences like IP bans or even civil lawsuits, particularly if an account is involved in the scraping process.
The legalities around data collection can vary depending on what kind of data you're targeting. Courts generally view scraping publicly accessible data (that doesn’t require login credentials) more leniently than accessing content protected by technical barriers. However, even public data isn’t entirely free from restrictions. Platforms may still enforce their own rules or take legal action. A notable example occurred in 2024 when X.com sued an Israeli company for allegedly bypassing anti-scraping measures. Although the case was dismissed due to insufficient legal grounds, it underscored the platform's firm stance on enforcing its terms.
Following Twitter's Terms of Service
To avoid legal trouble, start by checking Twitter's robots.txt file. This file outlines which parts of the site are accessible to automated tools. For instance, while /search is generally permitted, scraping /followers or /following lists is explicitly restricted. Additionally, use randomized delays (e.g., 2–5 seconds) between requests to avoid triggering anti-bot measures. Storing tweet IDs and timestamps can also reduce redundant requests, helping to minimize server strain and align your practices with Twitter’s policies.
Protecting User Privacy When Scraping
When handling Twitter data, user privacy should be a top priority. Focus on public metrics like likes, retweets, timestamps, and text that users have made publicly available. Avoid gathering sensitive details such as email addresses, phone numbers, or real names, as this could violate privacy laws. The European Data Protection Supervisor emphasizes the importance of limiting data collection to only what is necessary and implementing robust security measures to protect it.
For those conducting research within the EU, ensure compliance with GDPR by establishing a "legitimate interests" basis for your work. Document how the benefits of your research outweigh potential privacy risks. Additionally, regularly audit the data you collect and delete anything that is no longer needed to maintain ethical standards. This not only ensures compliance but also demonstrates a commitment to responsible data handling.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Data Extraction Method
Choosing the right method for extracting Twitter data depends on your technical skills, budget, and how often you need the data. TwitterAPI.io provides an easy-to-use option - no developer account approval necessary. It delivers both real-time and historical tweet data for $0.15 per 1,000 tweets, while also handling proxy rotation and CAPTCHA challenges.
If you're working on a one-time research project or have a limited budget, open-source libraries like Twikit or SNScrape can be a good fit. These tools are free but require coding knowledge and regular updates to keep up with Twitter's layout changes. As Cem Dilmegani, Principal Analyst at AIMultiple, explains:
"For one-off research, open-source is a great option. For ongoing Twitter data scraping, paid web scraping tools can reduce breakage and hidden costs".
While open-source tools save money upfront, they demand technical expertise and continuous maintenance.
For those who need complete control, DIY headless solutions like Selenium or Playwright might be the way to go. These methods let you customize your approach but come with high maintenance demands. You'll need to manage proxy rotation, add human-like delays (at least two seconds between requests), and constantly update your scripts to avoid detection. This approach is best suited for unique requirements that off-the-shelf tools can't meet.
Regardless of the method you choose, always follow legal and ethical guidelines. Use burner accounts instead of your primary profiles, stick to publicly available data, and comply with Twitter's Terms of Service.
FAQs
How does TwitterAPI.io compare to Twitter's official API in terms of pricing and features?
TwitterAPI.io offers a budget-friendly and flexible way to access Twitter data, standing out as an alternative to the official API. It enables users to gather data such as tweets, user profiles, and engagement metrics without dealing with the steep costs or stringent restrictions that often come with official API plans.
This platform provides a practical option for researchers, analysts, and developers who need dependable access to Twitter data while keeping expenses manageable.
What should I consider legally and ethically when scraping Twitter data?
When collecting data from Twitter, it’s crucial to stick to legal requirements and uphold ethical practices. Legally, ensure you’re only gathering publicly accessible information - like tweets or profiles that aren’t private or restricted. Steer clear of accessing protected content without proper authorization or breaking Twitter’s terms of service, such as bypassing rate limits or using overly aggressive scraping methods.
On the ethical side, respect user privacy by avoiding the sharing or resale of raw data without explicit permission. Use methods that reduce strain on the platform, like limiting the frequency of your requests and following robots.txt rules. Striking the right balance between your data needs, legal obligations, and ethical standards is key to mitigating risks and maintaining credibility.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of using code-based tools versus no-code tools to extract Twitter data?
Code-based tools, such as Python libraries like Snscrape or Twint, are perfect for tackling large-scale or intricate data extraction tasks. These tools let you automate workflows and customize data collection to match specific requirements. However, they do come with a learning curve - programming knowledge is a must. Plus, you'll need to handle technical setups and deal with ongoing challenges like CAPTCHA or rate limits.
In contrast, no-code tools are designed to be simple and accessible. They’re great for smaller, one-off data extraction projects and don’t demand any technical expertise. That said, they often fall short when it comes to scalability or offering advanced features. Additionally, these tools can struggle to bypass platform defenses, which might result in incomplete data.
Deciding between these options boils down to your technical skills, the complexity of your project, and how much data you need to gather.
Ready to get started?
Try TwitterAPI.io for free and access powerful Twitter data APIs.
Get Started Free