Real-Time Tweet Scraping: A Complete Implementation Guide
Real-Time Tweet Scraping: A Complete Implementation Guide
Real-time tweet scraping lets you access live tweets as they are posted. Using tools like TwitterAPI.io, you can filter tweets by keywords, users, or hashtags or analyze broader trends with random samples. This guide explains how to set up, connect, and process live tweet streams efficiently.
Key Takeaways:
- TwitterAPI.io simplifies streaming with WebSocket endpoints and REST APIs.
- Pricing: $0.15 per 1,000 tweets with a pay-as-you-go model.
- Setup Steps:
- Sign up and generate API keys (no approval needed).
- Test connections using Python and the
websocket-clientlibrary.
- Best Practices:
- Use filters (
from:username,#hashtag) to refine results. - Handle disconnections with backoff strategies.
- Process data in separate threads to avoid buffer issues.
- Use filters (
- Advanced Features:
- Add write actions like retweeting or replying.
- Use global infrastructure for low latency.
This article covers everything from setup to advanced scaling, ensuring you can manage high-volume streams and perform real-time analytics.
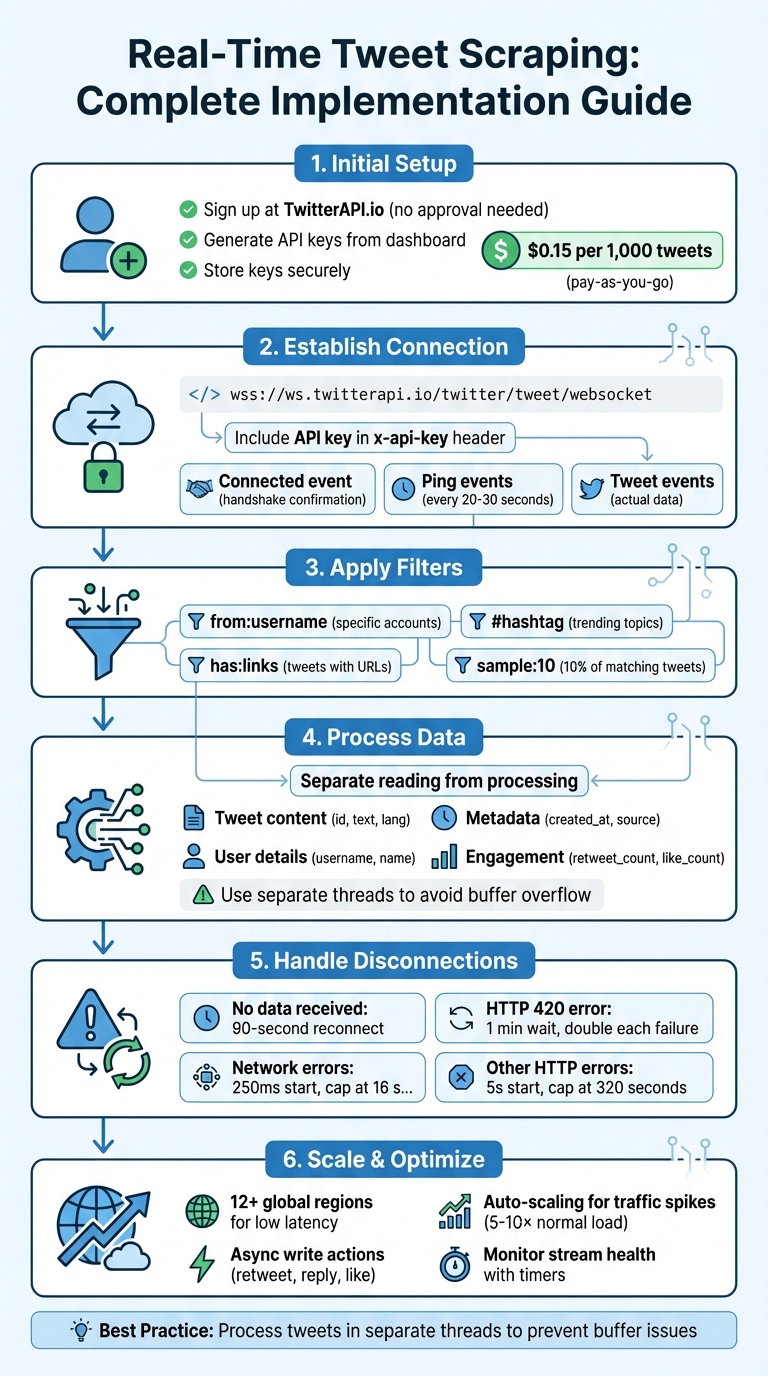
Real-Time Tweet Scraping Implementation Process with TwitterAPI.io
Setting Up TwitterAPI.io for Real-Time Streaming
Creating Your TwitterAPI.io Account
Starting with TwitterAPI.io is simple and doesn't involve the hassle of getting approval from Twitter's developer program, making it a great Apify alternative for Twitter. Just head over to the TwitterAPI.io website and sign up using your email. Once registered, you’re ready to go - no waiting required.
The platform operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which means you’re charged $0.00015 per tweet returned for successful requests and $0.00012 per API call when no tweets are found. This flexible approach ensures you only pay for what you use. Whether you're analyzing a handful of tweets for a small project or managing a large-scale operation processing thousands of tweets per second, this setup keeps costs manageable. For students and researchers with a .edu email address, TwitterAPI.io offers academic discounts - definitely worth reaching out to their team if you qualify.
To handle high traffic reliably, TwitterAPI.io automatically scales across 12 global regions, ensuring smooth performance even during peak usage.
Once your account is set up, the next step is generating and testing your API keys to establish a secure connection.
Generating and Testing Your API Keys
After signing up, navigate to the API keys section in your dashboard to generate your credentials. These keys are essential for authenticating your requests and connecting to TwitterAPI.io’s streaming endpoints. Make sure to copy and store your API key securely - you’ll need it for both REST API calls and WebSocket connections.
To test your authentication, include your API key in the X-API-Key header when making requests, such as to the endpoint https://api.twitterapi.io/twitter/tweet/advanced_search. For WebSocket streaming, connect to wss://ws.twitterapi.io/twitter/tweet/websocket and include your key in the x-api-key header. A successful connection triggers a connected event, confirming that everything is set up correctly. The server will also send periodic ping events to keep the connection active, and tweet events will deliver the data that matches your filter rules.
If you’re working in Python, the websocket-client library makes testing your connection straightforward. Running a quick test with this library ensures your credentials are properly configured before diving into building a full-fledged streaming application.
Building a Real-Time Tweet Streaming Application
Connecting via WebSocket Endpoints
WebSocket connections offer a persistent, two-way communication channel, making them perfect for real-time tweet streaming. Unlike traditional REST polling, WebSockets keep the connection open, pushing tweets to you instantly as they match your filters. This approach minimizes both latency and overhead.
TwitterAPI.io provides a WebSocket endpoint at wss://ws.twitterapi.io/twitter/tweet/websocket, which handles the complexities of maintaining the connection and delivering data. Once connected, the server sends three types of events: a connected event to confirm the handshake, periodic ping events to keep the connection alive, and tweet events containing the actual tweet data. To avoid timeouts, the server sends keep-alive signals every 20–30 seconds, so there's no need to implement a separate heartbeat mechanism on your end.
Writing Python Code for Real-Time Streaming
To build a streaming application in Python, you'll need the websocket-client library and a set of callback functions to handle various events. Specifically, you’ll need to manage four key events: connection, messages, errors, and disconnections. When a tweet event arrives, the JSON payload can be parsed to extract essential details like the tweet's ID, text, and author.
The core of the application revolves around defining an on_message function that uses json.loads() to parse incoming data. This function processes the tweets array, extracting fields such as id, text, and author. The on_open callback ensures your connection is ready, while on_error and on_close handle any disruptions. To establish the connection, configure the WebSocketApp with your API key in the x-api-key header. Finally, use the run_forever() method with a reconnect interval of roughly 90 seconds to automatically restore dropped connections.
Handling Common Streaming Issues
To keep your connection stable, it's crucial to separate data reading from data processing. As the X Developer Platform documentation highlights:
To avoid full buffer errors... your code should not do any real processing work as it reads the stream. Read the stream and then hand the activity to another thread or process.
If data consumption is too slow, the server's buffer can fill up, leading to forced disconnects.
Connection drops can occur due to various issues, such as network interruptions, server maintenance, or hitting rate limits. To handle these, implement a 90-second stall timer to reconnect if no data is received. For HTTP 420 errors, wait 1 minute before retrying and double the delay with each failure. For network errors, use a linear backoff starting at 250 ms, capping at 16 seconds. For other HTTP errors, apply exponential backoff, starting at 5 seconds and increasing up to 320 seconds. If the stream becomes too overwhelming, you can reduce the data flow by adding the sample: operator to your filter rules. For instance, sample:10 limits the stream to 10% of matching tweets.
Next, we’ll explore how to efficiently process and analyze the streamed data.
Processing and Analyzing Streamed Data
Extracting Key Tweet Fields
By default, TwitterAPI.io provides only the id and text of a tweet. To access additional details, you need to use the fields and expansions parameters. For instance, adding tweet.fields=created_at,public_metrics along with expansions=author_id (and user.fields=username,name) allows you to include timestamps, engagement metrics, and author information.
The streamed data arrives as JSON objects, where fields can appear in any order and may sometimes be missing, depending on the tweet's content. This means your parser should be flexible enough to handle unordered or absent fields. Timestamps are particularly useful for keeping track of stream lag.
| Field Category | Key Fields to Extract | Required Parameter/Expansion |
|---|---|---|
| Tweet Content | text, id, lang |
Default / tweet.fields |
| Metadata | created_at (timestamp), source |
tweet.fields |
| User Details | username, name, profile_image_url |
user.fields + expansions=author_id |
| Entities | hashtags, mentions, urls |
tweet.fields=entities |
| Engagement | retweet_count, reply_count, like_count |
tweet.fields=public_metrics |
Once these key fields are extracted, the next step involves refining the data set with specific filters.
Applying Filters for Keywords and Users
When setting filters, it’s important to first clarify your goals. Are you tracking updates from specific accounts, or are you more interested in monitoring broader trends? For focused monitoring, you can combine operators like from: for specific accounts, # for hashtags, and has:links to capture tweets that include URLs.
A good filtering strategy also involves deciding what data you don’t need. This helps refine your rules and improve efficiency. If a rule pulls in too much data, you can use the sample: operator (e.g., sample:10 to capture 10% of matching tweets). Filter rules can be updated asynchronously via POST requests, allowing you to add or delete them without disrupting your main stream connection.
With a well-filtered data set, you’re ready to dive into real-time analytics.
Running Real-Time Analytics
Once you’ve captured the filtered tweets, real-time analytics can help uncover trends and engagement patterns. For example, frequency analysis can highlight popular keywords or hashtags, while tracking metrics like retweets, replies, and likes can point to high-impact content. You can also study relationships, such as retweets and replies, to better understand how information spreads.
To avoid overloading your stream buffer, process the data in a separate thread as it arrives. Automated alerts can also be set up to monitor changes in data volume. A sudden drop might indicate network issues, while a spike could signal the need to adjust your filtering rules. Real-time dashboards are especially useful for visualizing tweet volume changes, acting as an early warning system for emerging trends or potential crises.
sbb-itb-9cf686c
Scaling and Advanced Features
Scaling for High-Volume Streams
Handling high-volume streams can get tricky - processing delays might cause buffer overflows and even disconnect your stream. To avoid this, offload each tweet immediately to a separate thread or queue for processing.
If the tweet volume starts to overwhelm your system, you can use the sample: operator (e.g., sample:10) to filter the stream down to 10% of its original volume. Another smart move? Set up automated monitoring to either remove high-volume rules or disconnect the stream once a certain data threshold is reached.
For applications where downtime isn’t an option, TwitterAPI.io offers redundant connections to keep the data flowing. Be prepared for sudden traffic spikes - sometimes up to 5–10× the normal load - by implementing exponential backoff strategies, especially in response to Error 420.
These approaches ensure your system stays solid and responsive, even when the data stream scales up dramatically.
Using Write Actions with Streaming
Once your stream is running smoothly under high volume, you might want to add write actions like posting replies, retweeting, or liking tweets. These actions can supercharge your automation, but there’s a catch: performing them directly in your stream-reading loop can slow things down and cause buffer issues.
To avoid this, handle write actions asynchronously using a task queue. This method keeps your stream-reading process uninterrupted and prevents delays from piling up. Keep in mind that write actions come with their own rate limits, so track these separately to steer clear of HTTP 420 errors.
Using Global Infrastructure for Better Performance
Routing your streaming connections through global infrastructure can significantly improve performance. TwitterAPI.io operates in 12+ global regions, letting you connect via the server closest to your application. This setup minimizes latency - often bringing it down to sub-second levels - and ensures smooth performance, even during high-traffic periods. Plus, the platform's auto-scaling capabilities handle sudden traffic surges without requiring extra capacity planning on your part.
To make the most of this global network, ensure your application respects DNS Time To Live (TTL) values. TwitterAPI.io may shift traffic between various IP addresses, and honoring TTL settings allows your connections to adapt quickly and seamlessly.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Summary of the Implementation Process
Setting up real-time tweet scraping with TwitterAPI.io is relatively simple if you follow a clear process. Begin by defining your goals - whether you’re tracking broad trends using sampled streams or focusing on specific topics with filtered streams. Then, ensure secure authentication and establish a persistent connection that remains open for continuous data flow. Use filter rules with operators like from:, has:links, or keywords to refine the stream to match your needs.
To avoid issues like "Full Buffer" errors that might cause disconnections, separate data ingestion from processing. Additionally, implement a robust reconnection strategy with backoff mechanisms to handle network issues, HTTP errors, or rate limits effectively. Following these steps will set you up for smooth and efficient real-time tweet scraping with TwitterAPI.io.
Tips for Successful Integration
Once your implementation is in place, these tips can help you fine-tune your integration for consistent, real-time performance.
Keep an eye on stream health by using an application-level timer to detect stalls and trigger timely reconnections. Monitoring tweet timestamps can also help you measure stream lag and ensure everything is running smoothly.
When building your parsers, account for variability in the data. JSON fields may appear in different orders, some fields might be missing, and duplicate messages could show up. If the data flow becomes too heavy, you can use the sample: operator (e.g., sample:10) to limit the stream to a more manageable rate. For applications handling large volumes of data, enable threading to keep your main application responsive while the stream operates in the background.
Lastly, pay attention to DNS TTL values. TwitterAPI.io operates across more than 12 global regions and can shift traffic between IP addresses. Respecting TTL settings ensures your connections adapt smoothly without disruptions. By following these practices, you’ll maintain a reliable, high-performance streaming setup with minimal latency.
Building a Twitter bot with Python p7 - Scraping Real-time Tweets
FAQs
What should I do if my connection drops while streaming tweets in real time?
If your connection drops while streaming tweets in real-time, having a plan to handle errors and reconnect is crucial. Set up your streaming client to recognize disconnections or errors and automatically attempt to reconnect after a brief pause. This helps ensure your data collection continues with as little downtime as possible.
To avoid abrupt interruptions, keep an eye on rate limits and manage exceptions carefully. These precautions allow your application to bounce back from network hiccups or API issues, keeping your live tweet stream steady and reliable.
What are the costs involved in using TwitterAPI.io for large-scale tweet scraping?
When it comes to high-volume tweet scraping, TwitterAPI.io offers an affordable option, especially since new users get 100,000 free credits to start. After using up those free credits, additional charges will depend on how much you use the service.
If you go the DIY route, managing your own proxies could set you back more than $10 per GB. On the other hand, Twitter's official API plans start at a hefty $42,000 per year. In comparison, TwitterAPI.io stands out as a more budget-friendly and accessible choice for businesses and researchers needing large-scale tweet data.
How can I gather detailed tweet data, including engagement metrics, using TwitterAPI.io?
With TwitterAPI.io, you can tap into detailed tweet data, including metrics such as likes, retweets, and replies. By using its API, you can connect to live data streams and retrieve engagement stats directly from public profiles and tweets in real time.
To keep your data collection running smoothly, it’s important to manage rate limits carefully and filter the data to match your specific goals. This way, you can easily integrate the information into your analytics workflows, whether for business insights or research projects.
Ready to get started?
Try TwitterAPI.io for free and access powerful Twitter data APIs.
Get Started Free