Real-Time vs Batch: Impact on Analytics
Real-Time vs Batch: Impact on Analytics
Real-time and batch data integration are two key approaches to managing data for analytics, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Real-time integration processes data as it's created, enabling immediate insights and actions. It's ideal for scenarios like fraud detection, live dashboards, and IoT monitoring, but requires higher infrastructure and operational costs.
- Batch integration processes large volumes of data at scheduled intervals, making it cost-efficient and perfect for tasks like payroll, financial reports, and historical trend analysis. However, it lacks the immediacy of real-time systems.
Key Insights:
- Real-time systems offer sub-second latency and are critical for time-sensitive applications, but demand more resources.
- Batch systems are simpler, more economical, and reliable for processing historical data but operate with higher latency.
- A hybrid approach combines the two, balancing immediate insights with long-term analysis.
Quick Comparison:
| Dimension | Real-Time Analytics | Batch Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Milliseconds to seconds | Hours, days, or weeks |
| Throughput | Continuous, record-by-record | High volume, grouped |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Data Freshness | Immediate | Delayed |
| Best For | Fraud detection, IoT, etc. | Payroll, reports, trends |
Choosing the right method - or a hybrid approach - depends on your business needs, balancing speed, cost, and complexity.
Real-time vs Batch Processing: A Beginner's Guide
sbb-itb-9cf686c
Real-Time Data Integration: How It Works and When to Use It
Real-time data integration processes information from multiple sources the moment it’s generated, pushing it into target systems with millisecond latency. Unlike batch processing, which works on scheduled intervals, this approach operates through an event-driven structure. Here, "producers" like apps or IoT devices generate events, while "consumers" - such as analytics platforms or dashboards - subscribe to them via a message broker [4,15]. Data can even be analyzed in transit, before it’s stored in a database.
The system relies on several technologies working together. Stream Data Integration (SDI) ensures continuous data flow into target systems, and Change Data Capture (CDC) tracks database changes like inserts, updates, or deletions to minimize network load. Tools such as Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, and cloud-native platforms like AWS Lambda handle the high-speed, fault-tolerant data streams needed for real-time integration [4,7,8]. This setup allows organizations to move from looking at past data to taking action in the moment - responding to events as they happen instead of hours or days later [3,4].
Key Features of Real-Time Data Integration
The standout feature of real-time integration is its ability to process data continuously with sub-second latency. For time-sensitive applications, operational data must be accessible within 1–2 seconds. During transit, the system validates, cleans, and transforms the data, ensuring downstream analytics receive consistent and reliable information [14,16]. This eliminates the delays and outdated insights typical of batch systems.
Another advantage is its ability to unify data from different systems without physically duplicating it. Data virtualization enables simultaneous access to multiple sources while maintaining 24/7 availability and fault tolerance. While this infrastructure requires more resources than batch processing, the benefits are clear. A 2024 study revealed that businesses leveraging real-time integration achieved 97% higher profit margins and 62% greater revenue growth compared to their peers.
Common Real-Time Data Applications
Fraud detection is one area where real-time integration is indispensable. Financial institutions must identify and block suspicious transactions as they happen, not after the fact [4,7]. Uber is a prime example of this approach. By July 2023, the company was processing over 30 billion messages daily using Apache Kafka for real-time driver matching, demand forecasting, and fraud detection [4,15].
Retail and e-commerce also thrive on real-time data. For instance, live clickstream data powers hyper-personalized recommendations and marketing offers [14,15]. Walmart’s inventory system processes 500 million events daily, delivering an up-to-the-minute view of stock levels across its global network of stores and distribution centers. In healthcare, real-time integration supports patient monitoring, triggering immediate alerts when vital signs like heart rate or blood pressure reach dangerous levels. Approximately 10% of hospitalized patients experience heart attacks, and predictive analytics can help identify these risks in advance.
Manufacturing and IoT applications use real-time data to predict equipment failures, analyzing sensor data such as turbine vibrations to schedule maintenance before issues arise [5,15]. Logistics companies rely on it for fleet tracking and route optimization, while ad-tech platforms use real-time integration for programmatic ad bidding, where each impression must be evaluated in milliseconds [5,17]. In all these cases, timely insights are critical, and real-time processing becomes a necessity rather than a luxury.
Batch Data Integration: How It Works and When to Use It
Batch data integration takes a different approach from real-time processing. Instead of handling data continuously, batch systems collect data over a set period or until a specific threshold is reached, then process it all at once as a single unit. This method maximizes efficiency by grouping data, making it ideal for handling large-scale workloads.
One of the biggest advantages of batch processing is its ability to reduce the number of individual input/output operations. By bundling records together, it optimizes network bandwidth through techniques like data compression. To further minimize system strain, organizations often schedule batch jobs during off-peak hours. Common workflows include ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) for structured data and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) for high-performance tasks in modern data warehouses like Amazon Redshift. As Christopher Tozzi from Precisely puts it, batch-based processing involves gathering data, storing it until a sufficient amount is collected, and then processing it all at once.
Technologies like Apache Hadoop (MapReduce), Apache Spark, and cloud services such as AWS Glue are commonly used to manage these large-scale batch operations. Among these, Apache Spark stands out for its faster performance, thanks to its in-memory computation capabilities. The main benefit of batch integration lies in its high throughput, which allows for the efficient handling of massive data volumes within a single processing window.
Key Features of Batch Data Integration
Batch integration plays a crucial role in analytics, particularly for historical trend analysis and reporting. It excels at processing large datasets when immediate results aren't necessary. By scheduling data processing at intervals - whether daily, weekly, or monthly - batch processing is perfect for tasks like generating monthly financial statements or summarizing daily sales data. This approach prioritizes simplicity and cost savings over low latency.
Its design is straightforward and fault-tolerant, making batch processing both reliable and economical. Errors can be identified and resolved before the final data transfer, and failed batch jobs can be restarted from a checkpoint, a recovery process that is much simpler than in streaming environments. It's no surprise that around 60% of organizations still rely on batch processing for their primary analytics needs.
Common Batch Data Applications
Batch processing is a cornerstone for generating long-term business insights through historical data analysis. It is widely used in business reporting and data warehousing. For example, companies often run nightly batch jobs to aggregate daily sales data, which is then loaded into data warehouses to support next-day business intelligence reporting. Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) systems, which handle complex historical reporting and trend analysis, depend heavily on batch processes to organize data into multidimensional schemas for identifying long-term patterns.
In financial services, batch processing is indispensable for tasks like monthly risk assessments, payroll processing, and reconciling end-of-day transactions. Billing systems also rely on batch processing to generate accurate monthly statements for utilities or credit cards. Similarly, regulatory compliance reporting and financial audits depend on batch systems because they prioritize the depth and accuracy of historical data over speed.
Other common uses include document indexing, data archiving, and trend analysis spanning multiple years. Many legacy enterprise systems are designed exclusively for batch processing, making it a critical part of hybrid IT setups where older and newer technologies coexist. Batch processing remains a cost-effective solution for analyzing large volumes of historical data, especially when the expense of maintaining a real-time pipeline outweighs the need for immediate insights.
Real-Time vs Batch Analytics: Main Differences
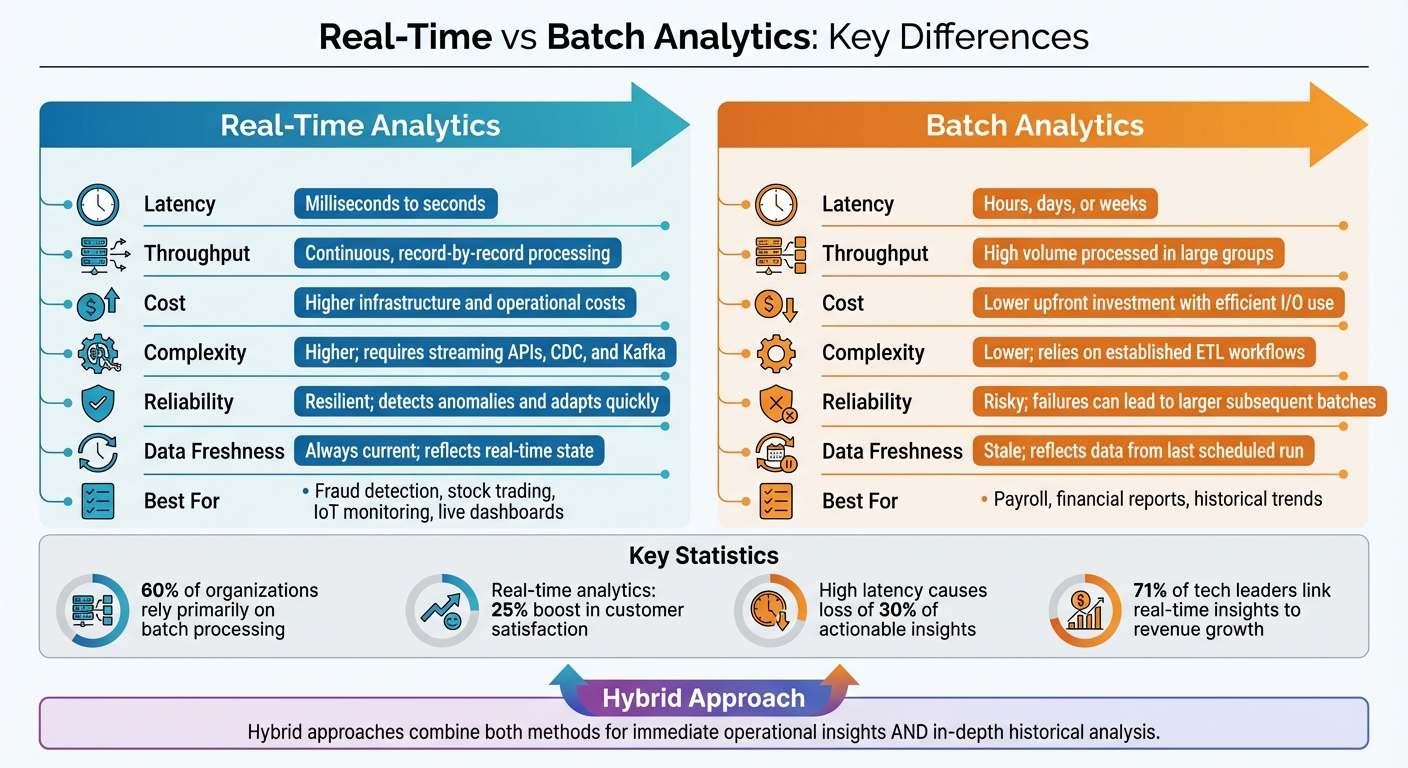
Real-Time vs Batch Analytics: Key Differences Comparison
The choice between real-time and batch analytics shapes how effectively your organization can respond to challenges and seize opportunities. At its core, the difference lies in timing: real-time analytics delivers insights within milliseconds to seconds, while batch analytics processes larger datasets over longer periods.
But speed isn't the only factor. You’ll also need to weigh infrastructure demands and costs. Real-time systems, which rely on tools like streaming APIs and Change Data Capture (CDC), provide instant insights but come with higher complexity and expenses. On the other hand, batch processing, often built on scheduled ETL workflows, is more cost-efficient but works with older data.
"In nearly every case, it's more valuable to have an answer now than it is to have an answer next week."
Batch systems may seem simpler, but they carry risks. For instance, if a batch fails, the next run can double in size, potentially overwhelming systems not built to handle such spikes. Real-time pipelines avoid this issue by processing data continuously, allowing for faster anomaly detection and smoother recovery from failures. These differences can significantly impact business outcomes.
High latency can lead to the loss of about 30% of actionable insights. Companies using real-time analytics report a 25% boost in customer satisfaction, thanks to faster responses. Additionally, many tech leaders link real-time insights to revenue growth. Despite these advantages, around 60% of organizations still depend primarily on batch processing. The table below highlights the key differences between these two approaches.
Comparison Table: Real-Time vs Batch Analytics
| Dimension | Real-Time Analytics | Batch Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Milliseconds to seconds | Hours, days, or weeks |
| Throughput | Continuous, record-by-record processing | High volume processed in large groups |
| Cost | Higher infrastructure and operational costs | Lower upfront investment with efficient I/O use |
| Complexity | Higher; requires tools like streaming APIs, CDC, and Kafka | Lower; relies on established ETL workflows |
| Reliability | Resilient; detects anomalies and adapts quickly | Risky; failures can lead to larger subsequent batches |
| Data Freshness | Always current; reflects real-time state | Stale; reflects data from the last scheduled run |
| Best For | Fraud detection, stock trading, IoT monitoring, live dashboards | Payroll, financial reports, historical trends |
This breakdown shows how choosing the right analytics approach is critical to aligning your data strategy with your business goals.
Hybrid Approaches: Using Real-Time and Batch Together
Why Hybrid Analytics Works
A hybrid approach combines the strengths of real-time and batch processing, offering the best of both worlds. With this method, you get immediate operational insights when timing is critical and in-depth historical analysis for strategic decision-making. This dual-layer design, often referred to as Lambda architecture, uses a streaming layer for instant, low-latency views and a batch layer to process late-arriving data, ensuring accuracy and completeness over time.
By reserving costly, always-on streaming for time-sensitive tasks and relying on batch processing for large-scale historical data, organizations can balance performance and cost-effectiveness. Platforms like Apache Iceberg simplify this process by allowing both streaming and batch systems to query the same governed tables, eliminating the need for redundant ETL steps.
"The hybrid approach provides the best features from both worlds (batch and streaming)." - Gaurav Thalpati and Bhavani Sudha Saktheeswaran, Onehouse
This balance is particularly evident in healthcare settings. For example, live patient vitals are streamed into alert systems for immediate action, while the same data is batched into Electronic Health Records for long-term clinical analysis. Similarly, fintech companies use real-time transaction streams combined with historical risk analysis to flag suspicious activity during processing, rather than after the fact. These examples highlight how hybrid systems tackle the challenges of both latency and throughput.
Example: Using TwitterAPI.io for Hybrid Analytics

Social media analytics is a great example of how hybrid approaches shine. Businesses use real-time feeds to track sentiment and identify trending topics instantly, while historical data is processed to analyze brand growth over time.
TwitterAPI.io supports this hybrid model by delivering real-time tweet streams for immediate insights alongside historical data for deeper analysis. Developers can monitor live tweets for urgent alerts and use batch queries for long-term sentiment studies. With a rate limit exceeding 1,000 requests per second and a global infrastructure spanning 12+ regions, the platform ensures smooth performance for both streaming dashboards and historical reporting.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Analytics Approach
Key Takeaways
Choosing between real-time, batch, or hybrid analytics comes down to aligning your integration strategy with your business objectives. For about 60% of organizations, batch processing is the go-to choice, offering a cost-effective way to handle tasks like payroll, billing, and historical reporting. On the other hand, real-time analytics is indispensable when speed is critical, with 71% of tech leaders linking it directly to revenue growth. High latency can result in losing 30% of actionable insights, while real-time integration has been shown to improve operational efficiency by 50%.
Latency requirements should guide your decision. For areas like customer experience, fraud detection, or trading operations - where immediate action is crucial - real-time integration can increase customer satisfaction by 25%. However, for less time-sensitive tasks, such as monthly risk assessments or quarterly reporting, batch processing offers a more cost-effective solution.
"In nearly every case, it's more valuable to have an answer now than it is to have an answer next week." - Ben Gamble, Enterprise & Solutions Marketing Lead, Aiven
Real-time systems require always-on architectures and come with higher resource costs, while batch processing works well with simpler, more resource-efficient setups. Interestingly, companies with scalable data strategies tend to expand their operations 20% faster than those with rigid systems. These insights highlight the importance of choosing the right analytics approach for your needs.
Final Thoughts
Looking ahead, the analytics landscape is shifting toward more flexible, hybrid strategies. By 2025, it's projected that 30% of all data will be consumed in real time, reflecting this industry evolution. While over 80% of businesses see real-time transformation as essential, only 12% have optimized their processes to fully leverage it. This gap presents both a challenge and an opportunity.
For many organizations, hybrid approaches offer the best of both worlds. Combining real-time insights for immediate action with batch processing for deeper, long-term analysis allows businesses to address both operational and strategic needs. Start small - focus on one high-value use case, set clear service level objectives, and identify potential failure points before scaling. For example, platforms like TwitterAPI.io are designed to support hybrid strategies, delivering both real-time and historical data seamlessly.
FAQs
What should I consider when deciding between real-time and batch analytics?
The choice between real-time and batch analytics boils down to how quickly you need insights. Real-time analytics shines in situations where immediate action is critical - think fraud detection, stock trading, or live customer interactions. It processes data almost instantly, enabling split-second decisions. In contrast, batch analytics is better suited for scheduled tasks, like creating daily reports or examining historical trends. It's also typically easier on the budget.
Another key consideration is data volume and latency needs. Batch processing is great for handling large datasets by processing them in chunks, though it comes with delays that make it less ideal for time-sensitive scenarios. Real-time analytics, on the other hand, reduces delays significantly, offering instant results. However, this speed often comes with a need for more complex systems and higher costs. Many organizations find that a hybrid approach - combining the strengths of both methods - can strike the right balance for their specific needs.
How does combining real-time and batch processing improve data analytics?
Using a mix of real-time and batch processing brings together the strengths of both methods for data analytics. Real-time processing allows for instant insights by analyzing data as it comes in, making it perfect for decisions that need to be made quickly. Meanwhile, batch processing excels at managing large sets of historical data, offering a way to uncover trends and plan strategically.
When these two approaches are combined, organizations can benefit from quicker decision-making powered by real-time insights, while also relying on batch processing for a deeper analysis of past data. This blend improves efficiency, minimizes delays, and provides a more comprehensive understanding of the data, enabling both quick responses and long-term planning.
What are the key challenges and solutions for implementing real-time data integration?
Real-time data integration isn’t without its hurdles. Challenges like managing latency, navigating system complexity, and ensuring data quality can make it a daunting task. Delivering data in near-instant timeframes - whether seconds or minutes - demands a solid infrastructure and finely tuned processes. On top of that, setting up continuous data feeds can stretch IT resources thin, and the rapid flow of information increases the chance of errors or incomplete data sneaking through.
To overcome these obstacles, organizations can turn to advanced tools and smart strategies. For instance, streaming platforms like Apache Kafka are great for handling data with minimal latency while keeping its integrity intact. Beyond technology, it’s crucial to establish clear data transformation rules, carefully plan IT capacity to avoid bottlenecks, and set up robust monitoring systems to catch and correct issues. With thoughtful preparation and the right tools in place, real-time data integration becomes much more manageable.
Ready to get started?
Try TwitterAPI.io for free and access powerful Twitter data APIs.
Get Started Free