Historical Tweet Data: 5 Methods to Access Past Content
Historical Tweet Data: 5 Methods to Access Past Content
If you want to find old tweets, there are five main ways to access them. Each method has different costs, ease of use, and data limits:
- Twitter Advanced Search: Free and simple but manual. Best for finding specific tweets, not bulk data.
- Twitter Full-Archive Search API: Paid, requires a developer account. Ideal for programmatic access to large datasets.
- TwitterAPI.io: Paid, starting at $0.15 per 1,000 tweets. Easier setup than Twitter's API and good for flexible, large-scale needs.
- Third-Party Data Archives: Free or paid. Offers pre-collected datasets, often for academic research or major events.
- Scraping Tools (e.g., Snscrape): Free but technical. Requires coding skills and may face limitations due to platform defenses.
Each option fits different needs, whether you're a casual user, developer, or researcher. Below is a quick comparison to help you decide.
Quick Comparison
| Method | Cost | Ease of Use | Data Limits | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Twitter Advanced Search | Free | Easy (Manual) | Low (Small Searches) | Finding specific tweets |
| Full-Archive Search API | Paid (Pro or higher) | Moderate (Tech) | High | Developers and researchers |
| TwitterAPI.io | $0.15/1,000 tweets | Easy (Fast Setup) | High | Businesses needing flexibility |
| Third-Party Archives | Free or Paid | Moderate | Varies | Pre-collected datasets |
| Snscrape | Free (Open-source) | Hard (Coding) | Medium | Budget-friendly coding projects |
Choose based on your technical skills, budget, and how much data you need.
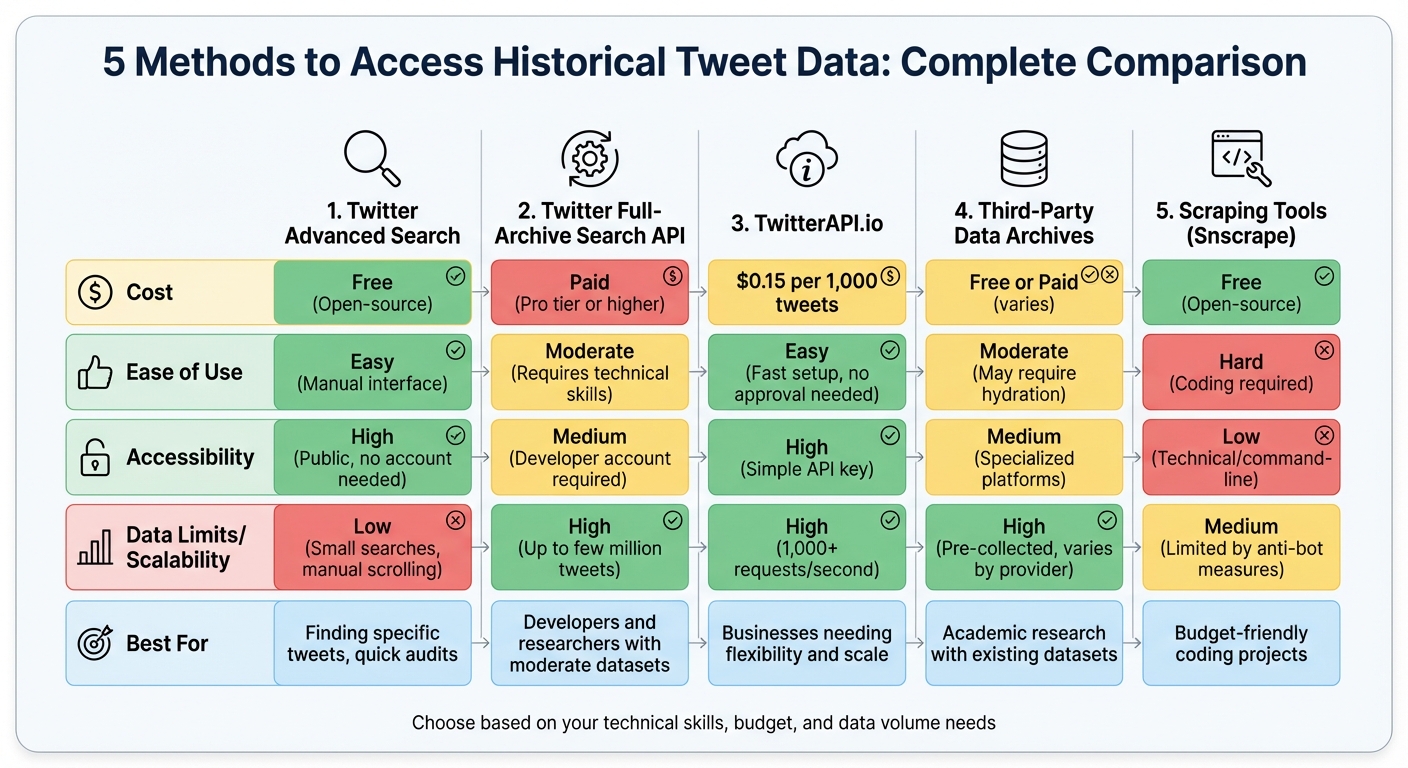
Comparison of 5 Methods to Access Historical Twitter Data
1. Twitter Advanced Search
Twitter's Advanced Search is a powerful, free tool that lets you dig through the platform's entire archive, going all the way back to March 21, 2006. The best part? You don’t need to be a tech wizard or have API access - just head over to twitter.com/search and get started.
Accessibility (manual or programmatic)
This tool is entirely manual. To access it, click the three-dot menu next to the search bar and select Advanced Search. From there, you’ll find fields to customize your search, like exact phrases, hashtags, usernames (via from:, to:, or mention operators), and date ranges using since: and until:. You can also filter by language with lang:en and use Boolean logic - combine terms with spaces for AND, use OR for alternatives, and exclude terms with a dash. If you’re comfortable typing directly into the search bar, you can skip the interface entirely. For example, try something like: from:elonmusk since:2010-01-01 until:2015-12-31.
Cost (free or paid options)
The Advanced Search interface is 100% free for anyone with a standard X account. There are no fees or hidden charges, and you can perform as many manual searches as you like. However, keep in mind that there’s no built-in option to export search results into formats like CSV or JSON, so everything has to be handled manually.
Scalability (volume of tweets retrievable)
This tool works best for small-scale searches. Since results are paginated and require manual scrolling, it’s not ideal for gathering large datasets. If you’re looking to analyze thousands - or even millions - of tweets, you’ll need to explore programmatic tools that can handle bulk data collection. You can also find essential resources and tools to help you scale your data gathering efforts. This method is better suited for finding a few hundred tweets at most.
Ease of Setup and Use
Getting started is a breeze. The interface is user-friendly and doesn’t require any technical know-how. You can refine your searches with operators like lang:en to focus on specific languages or narrow down results by engagement metrics like likes or retweets. It’s an excellent option for anyone looking to surface historical content without diving into complex tools or coding.
2. Twitter Full-Archive Search API
The Full-Archive Search API is a powerful tool designed for developers who need to handle large datasets programmatically. Unlike Twitter's Advanced Search, which is more manual, this API automates the process of retrieving data, making it ideal for those who require access to Twitter's extensive historical data.
Accessibility (manual or programmatic)
This API is entirely programmatic, meaning you'll need an approved developer account through the X Developer Portal to get started. Once your account is set up, you'll generate API keys and a Bearer Token for authentication. Access is available via Twitter API v2 at the Pro tier or higher, the Academic Research track, or through Enterprise-level accounts. For Enterprise access, you'll need to coordinate directly with Twitter's sales team. Requests are made using tools like cURL or other HTTP clients, with authentication handled through the Bearer Token for v2 users or username/password for Enterprise Gnip endpoints. Keep in mind, this tool follows a pay-per-use pricing model.
Cost (free or paid options)
The Full-Archive Search API doesn’t offer a free tier. At a minimum, you’ll need to subscribe to the Pro-level plan or secure an Enterprise contract. The pricing follows a pay-per-use model, where every request - even those made for pagination - is billed. Enterprise accounts typically require a 12-month subscription commitment.
Scalability (volume of tweets retrievable)
This API is built to handle large volumes of data but is best suited for datasets containing a few million tweets or less. Each request retrieves up to 500 tweets, and you can use the next_token to paginate through larger datasets. Standard accounts allow 300 requests every 15 minutes (approximately 1 request per second), while Enterprise users typically get 120 requests per minute. For extensive data retrieval, such as pulling tweets from an entire year, making parallel requests can help speed up the process. Note that standard query lengths are capped at 1,024 characters, while Enterprise users enjoy an extended limit of 4,096 characters.
Ease of Setup and Use
Using this API requires familiarity with RESTful APIs, authentication processes, and techniques for managing pagination and handling errors. For example, if you encounter a 503 error, you’ll need to implement retry logic or adjust your query's time window - such as narrowing it down to a 6-hour range. On the bright side, the API supports advanced query operators like is:retweet, lang:, and has:images, allowing you to fine-tune your searches and avoid wasting credits on irrelevant data. While this tool is extremely powerful, it does demand a solid understanding of API workflows and troubleshooting.
3. TwitterAPI.io Historical Tweet Data

TwitterAPI.io provides a straightforward way to access historical tweet data using its Advanced Search API. Unlike Twitter's official process, which often involves extensive developer approvals, this service simplifies the experience. It’s tailored for developers looking for a reliable and flexible solution to retrieve historical tweets using programming languages like Python, Node.js, or Java. Essentially, it bridges the gap between manual searches and the complexity of official Twitter endpoints.
Accessibility (manual or programmatic)
TwitterAPI.io offers programmatic access through a REST API. Getting started is simple: sign up, grab your API key, and you’re ready to make requests. The platform even provides pre-written code snippets to help you integrate the API into your projects right away. There’s no need to deal with the hassle of developer account approvals or complicated authentication processes - your API key is all you need.
Cost (free or paid options)
The service uses a recharge-based pricing model, starting at $0.15 per 1,000 tweets. New users can take advantage of a free trial, which includes access to historical data but comes with stricter Twitter API rate limits. Once your trial credits are used up, you can simply add funds to continue. With its pay-as-you-go structure, you only pay for what you use - there are no monthly subscriptions. Additionally, academic users with a .edu email can apply for discounted rates, making it a budget-friendly option for both small-scale and large-scale projects.
Scalability (volume of tweets retrievable)
This platform is designed to bypass the typical 800–1,200 tweet pagination limit seen in standard searches. By using the max_id parameter, you can retrieve large datasets without running into artificial restrictions. Free trial accounts allow one request every five seconds, while paid accounts can handle up to 20 requests per second. For extensive data collection, you’ll need to implement max_id pagination in your code and use a set to track tweet IDs, ensuring you avoid duplicates.
Ease of Setup and Use
Setup is quick and user-friendly, taking just a few minutes. The API supports advanced search operators, allowing you to refine your queries with precision. The data returned includes full metadata - engagement metrics, complete tweet text, and user information - giving you everything needed for in-depth analysis without requiring additional requests.
4. Third-Party Data Archives and Datasets
Third-party archives provide a convenient way to access historical tweet datasets. These archives include resources like academic repositories, open-source platforms, and specialized data providers. They often offer pre-packaged datasets in formats like CSV or JSON, ready for analysis, machine learning projects, or research.
Accessibility (Manual or Programmatic)
Most archives make it easy to download datasets manually through user-friendly web interfaces. For instance, TweetSets from George Washington University provides a simple interface to search datasets and download tweet IDs. Some collections, like those covering events such as Hurricane Irma, include over 17 million tweets.
For more advanced users, some providers offer programmatic access. This might include SQL-based querying or batch job systems that allow you to request datasets and receive large files for bulk download. A good example is the Wharton Research-IT database, where users can run SQL queries against a 1% sample of historical tweets.
Cost (Free or Paid Options)
There are both free and paid options, depending on your needs. Platforms like Sigma.AI offer open-source datasets that are publicly available, while TweetSets provides free access to extensive collections focused on major events. On the other hand, commercial services like Tweet Binder charge fees based on the number of tweets and the historical range. For example, Tweet Binder offers a free preview report covering 7 days and up to 200 tweets. As Javier Abrego, Founder and CEO of Tweet Binder, explains:
"The price of Historical Twitter data always depends on two things: Number of old tweets [and] Number of days back".
Scalability (Volume of Tweets Retrievable)
The amount of data you can retrieve depends on the provider. Commercial tools often limit individual reports to around 35,000 tweets, while academic archives can provide datasets with millions of tweets - though these are usually tied to specific events already compiled. For example, the Wharton database offers a continuous 1% sample of all tweets, which is great for trend analysis but may not suit high-precision studies. Additionally, many free datasets only include "dehydrated" tweet IDs, meaning you'll need to hydrate them separately to access the full tweet content.
Ease of Setup and Use
Using these archives is generally straightforward. Platforms like TweetSets make it easy to search, filter, and download data with minimal effort. However, there are a few things to consider. Some datasets may only include tweet IDs, requiring hydration, while others might come in large batch files segmented into 10-minute intervals, which need further processing. If you're considering a paid service, try using free preview tools first to check data quality and ensure the metadata includes the engagement metrics you need.
This approach offers an alternative to scraping tools, which will be discussed in the next section.
sbb-itb-9cf686c
5. Scraping Tools like Snscrape
Scraping tools offer a way to access historical tweets without spending a dime. One such tool, Snscrape, is a Python-based scraper that lets you retrieve tweets and their metadata by specifying date ranges. This functionality makes it possible to tap into Twitter's full archive.
Accessibility
Snscrape operates programmatically, meaning it’s designed to work through command-line interfaces or as part of Python scripts. Unlike tools with web dashboards, it requires some coding knowledge. Installation is straightforward: use pip with Python 3.8+ or download it directly from its GitHub repository. Compared to the official APIs, which can involve a more intricate setup, Snscrape is relatively user-friendly for those familiar with coding.
Cost
Snscrape is completely free and open-source, distributed under the MIT license. This makes it an affordable alternative to official API tiers, which often come with pay-per-use or credit-based pricing structures [12, 22]. The volume of tweets you can retrieve depends on your system’s execution speed and Twitter’s rate limits, but there are no extra charges.
Scalability
If you’re looking to speed things up, you can use multithreading techniques. However, Twitter’s anti-bot defenses - like captchas and IP bans - can pose challenges when scraping on a large scale [22, 23].
Ease of Setup and Use
For Python users, getting started is relatively simple. Once installed, Snscrape lets you filter tweets by language, specific user accounts, or even exclude replies. You can export the collected data into formats like Pandas DataFrames or CSV files. Keep in mind, though, that if Twitter changes its interface, you might need to tweak your scripts slightly [22, 23].
Method Comparison Table
When choosing a method, think about your skills, budget, and how much data you need. Here's a quick comparison of five popular options:
| Method | Cost | Accessibility | Scalability | Setup Requirements | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Twitter Advanced Search | Free | High (Public) | Low (Manual) | None | Quick audits, finding specific old tweets |
| Twitter Full-Archive Search API | Paid (Pro+) | Medium (Dev Account) | High | High (Coding/API Keys) | Low-volume datasets under a few million tweets |
| TwitterAPI.io | $0.15 per 1,000 tweets | High (No approval needed) | High | Low (Fast setup) | Businesses needing flexible, affordable access |
| Third-Party Data Archives | Free/Paid | Medium (Specialized) | High (Pre-collected) | Medium (Hydration tools) | Academic research with existing datasets |
| Scraping Tools (Snscrape) | Free (Open-source) | Low (Technical) | Medium | High (Coding/Proxies) | Budget-constrained projects with coding skills |
Each method has its own strengths, as explored earlier in the article. This table brings those insights together for a quick side-by-side comparison, helping you choose based on your specific needs.
For large-scale data collection, TwitterAPI.io stands out. Its infrastructure can handle over 1,000 requests per second with auto-scaling, making it ideal for high-volume projects without the hassle of managing batch jobs. On the other hand, the Full-Archive Search API may not be the best option for extremely high-volume needs due to its efficiency limitations.
If you're on a tight budget, Twitter Advanced Search or open-source tools like Snscrape can save costs, though scraping tools may face restrictions due to Twitter's anti-bot measures. For businesses that prefer processed data without coding, TwitterAPI.io offers a straightforward pay-as-you-go model starting at $0.15 per 1,000 tweets.
Academic researchers should consider applying for Twitter's Academic Research product track, which provides access to full-archive search capabilities dating back to March 2006. Additionally, TwitterAPI.io offers discounts tailored for academic use, making it an appealing option for research-focused projects.
Conclusion
Different methods for accessing historical tweet data cater to varying needs, from quick searches using Twitter Advanced Search to programmatic access with the Full-Archive Search API for smaller-scale datasets.
For those looking for a straightforward, flexible option, TwitterAPI.io stands out with its pay-as-you-go model, priced at $0.15 per 1,000 tweets. It eliminates the hassle of lengthy approvals or long-term contracts and boasts the ability to handle over 1,000 requests per second across 12+ global regions. Whether you're working on a small audit or pulling extensive datasets, this solution simplifies the process without the headaches of enterprise sales or per-request billing.
That said, other options remain valuable. Developers and researchers might turn to third-party archives or open-source tools like Snscrape - though managing anti-bot measures is a consideration. The official Twitter API v2 provides modern metadata, such as edit history and conversation threads, through a pay-per-usage pricing model. For large-scale projects, the Historical PowerTrack offers batch processing with up to 1,000 rules at once, though it typically requires a year-long subscription.
Each approach has its strengths, ensuring there's a tool to match every project's unique requirements.
FAQs
What makes TwitterAPI.io a great choice for accessing historical tweet data?
TwitterAPI.io shines in its ability to deliver extensive access to historical tweet data, bypassing the usual pagination limits. By leveraging features like the max_id parameter, it enables users to pull a larger, more detailed dataset. This makes it an excellent resource for tasks like in-depth research, detailed analysis, or uncovering business insights.
The platform simplifies the process for developers by providing ready-to-use code examples in popular languages such as Python, Node.js, and Java. Additionally, its support for advanced search operators allows users to refine their queries with precision. You can filter by keywords, hashtags, user attributes, or date ranges to zero in on exactly what you need. Whether you're monitoring trends, performing sentiment analysis, or diving into academic research, TwitterAPI.io equips you with the tools to easily access and analyze historical Twitter data.
What are the cost and scalability considerations for using the Twitter Full-Archive Search API?
The Twitter Full-Archive Search API offers access to every tweet ever posted, starting from March 2006. This makes it an incredibly useful resource for digging into historical data. However, it’s important to note that this API is usually included in Twitter's research or enterprise-level plans, which often come with higher costs and specific access conditions.
This tool is well-suited for large-scale projects or organizations that require advanced data capabilities. But for smaller budgets or casual users, it might not be the most practical option. Be sure to assess your project’s goals and financial constraints to see if this API is the right fit for your needs.
What challenges come with using scraping tools like Snscrape to access historical tweets?
Scraping tools, such as Snscrape, can offer a quick way to extract data, but they come with some notable limitations. For one, these tools often can't provide access to the complete archive of tweets, especially older posts, leading to gaps in the data. There's also the risk of running into compliance issues, as scraping methods may breach Twitter's terms of service, potentially resulting in blocked access or interruptions.
Unlike official APIs, scraping tools lack advanced capabilities like detailed filtering options, comprehensive metadata, and support for more complex queries. This makes them a less reliable choice for businesses or researchers who need accurate, reliable, and compliant access to historical Twitter data. For those needs, official solutions like Twitter's full-archive search API are far better equipped.
Ready to get started?
Try TwitterAPI.io for free and access powerful Twitter data APIs.
Get Started Free